Artificial intelligence (AI) vs. machine learning: what a business needs to know
Although there are many technological trends in 2025, AI and ML are the most prominent discoveries affecting nearly all industries. They revolutionize industries by reducing costs, increasing profits, and uncovering new opportunities. It’s like getting the Eye of Providence for your business.
Various sources indicate that AI and ML help businesses become more competitive and innovative. The adoption of AI has already soared from 55% in 2023 to 72% in 2024. What’s more, early AI adopters realize performance gains of up to 20% of earnings in the first 18 to 36 months.
But what’s the difference between AI vs machine learning? Can they be used interchangeably? In this article, we’ll compare machine learning vs artificial intelligence. You’ll learn about the possible benefits and features both technologies can bring to your business. Read on for more!
What is artificial intelligence (AI)?
Artificial intelligence is a field of computer science that enables a machine to mimic intelligence. AI programs can perform complex tasks traditionally requiring human learning, reasoning, and other skills. Let’s delve into AI types and find out more about the key use cases.
Narrow (“weak”) AI
Narrow AI is designed to solve specific problems and complete a limited range of tasks. One of the examples here is chatbots. You can’t ask them to detect fraud in financial transactions, but they can help you get certain information related to the service.
General (“strong”) AI
General AI is an intelligent computer system that can perform tasks, even complex ones, as well as humans do. For now, AGI exists only in theory, as it would require a wide range of capabilities packed into a single program.
Key applications
Although AI has multiple use cases across various business functions, this game-changer has several distinct features that are used nearly everywhere. The primary use case is customer service. You’ve definitely communicated with chatbots, virtual assistants, and other GPT-like tools that can maintain an adequate conversation. That’s how AI works.
Some other use cases include business intelligence to analyze and visualize data, document processing to extract structured and unstructured data, etc. However, all this requires machine learning to train the AI models and maximize their efficiency.
What is machine learning (ML)?
Machine learning is a technology used to analyze and learn from historical data and build upon known patterns to predict future events. A machine learning computer system finds these patterns by running statistical algorithms on training datasets. Let’s see the types of ML and their applications.
Types of machine learning
Based on their learning types, ML models can be built using three main approaches:
- Supervised learning: Training datasets contain inputs and desired outputs; the model learns a general rule for producing desired outputs;
- Unsupervised learning: Training datasets contain no labels; the model has to determine the patterns in the input on its own;
- Reinforcement learning: The model is presented with an objective to complete in a test environment; it receives feedback in the form of rewards or penalties and seeks to maximize rewards.
Key applications
Machine learning has its fair share of use cases, proving to be a pivotal tool in transforming business operations and strategies. Its primary application is big data analytics, which allows businesses to predict customer needs and deliver personalized experiences at scale.
It’s also a great tool to predict sales, analyze risks, and generally use historical data to uncover trends and possibilities. While it may seem similar to AI, there is quite a big difference between these two technologies. Let’s take a look at artificial intelligence vs machine learning in more detail.
Comparing machine learning vs AI
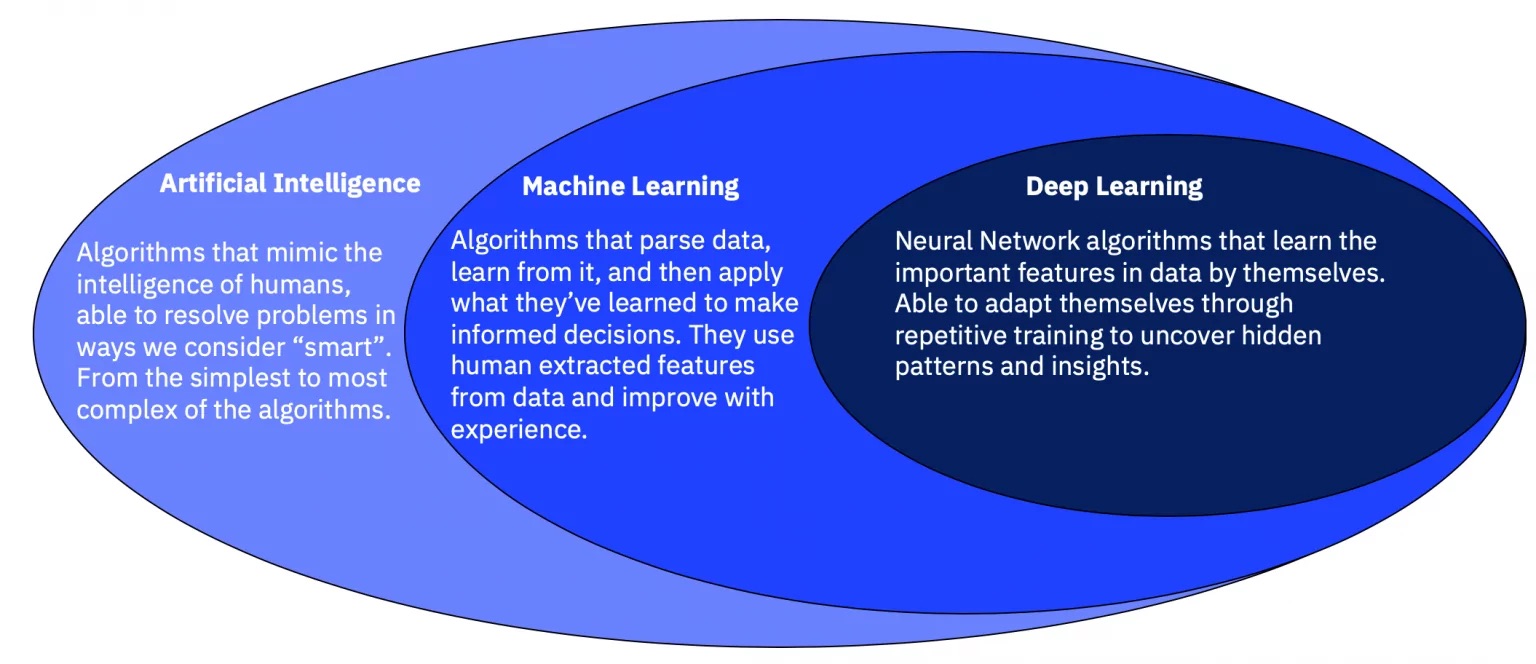
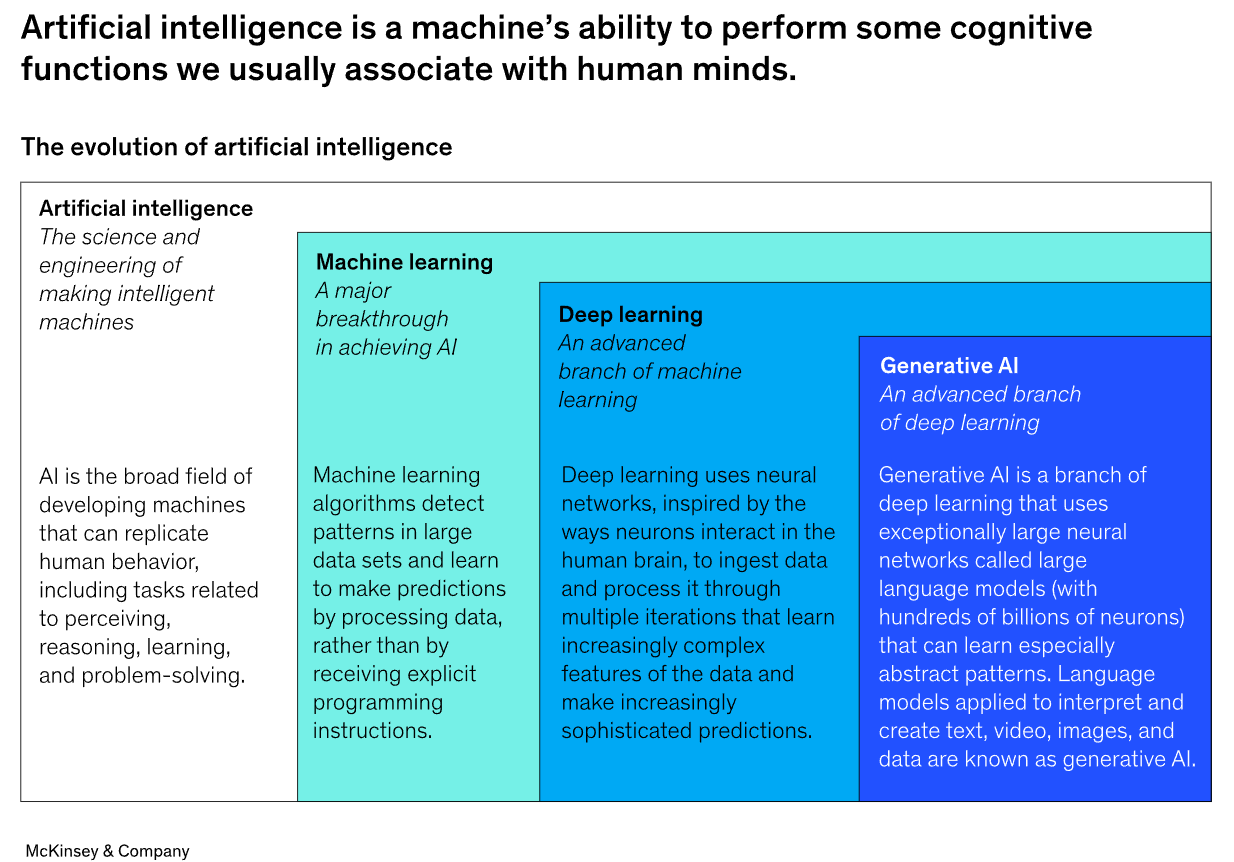
The main difference between machine learning and artificial intelligence is based on their scope and focus. If we analyze these in detail, we’ll get the following definitions:
- Artificial intelligence is a broader category that focuses on creating systems capable of performing tasks that would typically require human intelligence. This includes reasoning, decision-making, problem-solving, natural language understanding, perception, and more.
- Machine learning is a subset of AI that focuses on enabling systems to learn and improve from data without being explicitly programmed for every task. ML algorithms identify patterns in data and use them to make predictions or decisions. It’s the foundation of AI.
Does it seem too complicated? Think of AI as the goal. ML will be one of the paths to achieving this goal, helping you teach machines from data and turn them into full-fledged artificial intelligence.
Usually, both options go along together. But there are certain cases where this differs. AI is used to automate complex processes and improve decision-making based on big data. ML is used to predict trends and automate simple processes.
We’ll describe the possible use cases for each in the following section.
How AI and ML are used across industries
With the difference between AI and machine learning broken down, let’s explore the key applications for AI vs ML technologies across four industries. Although there are many possible use cases, they are generally based on automation and data analysis.
Finance
AI
In finance, 48% of organizations already leverage artificial intelligence in operations, and 45% use it in risk and compliance. Common uses of AI in finance include:
- Automating risk management. AI can summarize thousands of pages of new regulations (e.g., Citigroup) and power virtual assistants that can answer compliance questions. It can also generate reports and automate compliance checks.
- Creating intelligent trading systems. AI-powered trading systems can help people find the best conditions for deals and automatically sell or buy stocks. It’s a win-win situation for volatile markets and the never-ending news flow in our world.
ML
49% of companies are already using or planning to use ML in their operation. This is due to the multiple use cases in their industries:
- Forecasting market conditions. HSBC USA’s AiPEX, which is one of the world’s best ML-powered stock indexes, outperformed the S&P 500 by 123% over the past decade. At the same time, JPMorgan used deep neural networks to automatically determine the most profitable way to execute trades.
- Assessing risks during underwriting. Machine learning models can promptly assess customer solvency and credit risks. For example, Rocket Mortgage’s system saves its employees over 5,000 hours of manual work a month. Such tools are used globally across various businesses.
Insurance
AI
In insurance, machine learning and AI speed up claim management, enhance risk management, and improve customer experiences. Here’s how AI implementation can transform insurance services:
- Automating document processing. Computer vision can extract data from documents, images, and videos to speed up underwriting and claim processing.
- Improving customer service. AI-powered robo-advisors and virtual assistants are already facilitating policy and claim management (e.g., Lemonade’s AI Jim and Zurich Insurance’s Zuri).
ML
The ML market in insurance was evaluated at $8.13 billion in 2024. Companies use machine learning for:
- Fraud detection and prevention. Machine learning algorithms can flag potential fraud in underwriting and claims and autonomously identify new fraud schemes.
- Faster claim processing. Machine learning can analyze claims data and calculate the appropriate payouts faster than humanly possible. For example, Lemonade set the record with a two-second claim settlement.
Marketing and customer interaction
AI
While the difference between machine learning and AI is quite pronounced, marketing and customer interaction are fields where the two technologies are often used in tandem:
- Personalized customer experiences. AI can automate personalization at scale, serving all customers as a segment of one based on customer data analysis by machine learning models.
- Chatbots and virtual assistants. Thanks to generative AI, chatbots, and virtual assistants have become more lifelike and flexible.
ML
Did you know that Netflix saved $1 billion in 2017 by using machine learning for personalized recommendations? That’s only one of the ways ML can help in marketing:
- Analyzing customer behavior. Machine learning can analyze swaths of data to segment customers and optimize customer journeys. For example, Starbucks’ Deep Brew used data-driven optimization to grow its reward program and promote customer loyalty.
- Predicting customer needs and preferences. Machine learning models can forecast customer needs and even the likelihood of churn. Builderbuild, for instance, leveraged it to identify at-risk accounts – and reduced customer churn by 60%.
Manufacturing
AI
Over half of manufacturers have already implemented at least one AI use case. So, if you need some examples of AI vs. ML in manufacturing, here’s how manufacturers use artificial intelligence.
- Automating manufacturing processes. Amazon heavily automates its operations with a fleet of 750,000 cobots, or collaborative robots. These cobots work together with employees to speed up operations while minimizing human error.
- Automating quality control. For example, Google’s Visual Inspection AI uses ultra-high resolution images of up to 100MB to detect the tiniest of defects in manufactured items.
ML
The ML market in manufacturing was estimated at $921.3 million in 2022, proving its popularity in the industry. Here’s how companies usually apply machine learning in this industry:
- Predict equipment failures. Machine learning solutions can predict when a failure becomes likely and signal the need for maintenance. This minimizes planned and unplanned downtime.
- Optimize resource allocation. Machine learning algorithms can forecast order volumes and identify the most suitable fulfillment options. For example, IBM’s own machine learning tool, Fulfilment Optimizer, analyzes past and real-time data to optimize fulfillment, reducing costs and boosting operational efficiency.
As you can see, many industries can benefit from AI and ML in various ways. But these technologies aren’t perfect and omnicapable. They have their strengths and weaknesses as well, so we’ll cover them in the next section.
Advantages and limitations of AI and ML
Both artificial intelligence and machine learning can bring substantial benefits to adopters – but their limitations have to be addressed, too. Here are the pros and cons of both options.
AI and ML offer complementary strengths for businesses. While AI excels at automating complex processes and improving decision-making, ML is ideal for extracting insights from data and adapting to dynamic environments. Both empower businesses to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and drive innovation.
What to choose: artificial intelligence or machine learning?
As you can see, artificial intelligence and machine learning are quite different. AI is great for complex solutions with enhanced decision-making and automation; ML is the perfect choice for extracting insights from data and adapting to new environments.
If you want to leverage the benefits of both technologies in your industry, get in touch with our experts to get a consultation. We’ll help you choose the best solutions for your business and bring all your ideas to life. It’s time to bring innovation to your company!

Similar articles
More about Product developmentStay updated with the latest case studies

